Measuring Impacts of Poisoning on Model Parameters and Embeddings for Large Language Models of Code
Software Engineering Research Group
University of Houston
account_balance Supported by National Science Foundation
event Accepted at The 1st ACM International Conference on AI-powered Software (AIware 2024), co-located with the ACM International Conference on the Foundations of Software Engineering (FSE 2024), Porto de Galinhas, Brazil
arrow_backReturn to Safe and Explainable AI Projects
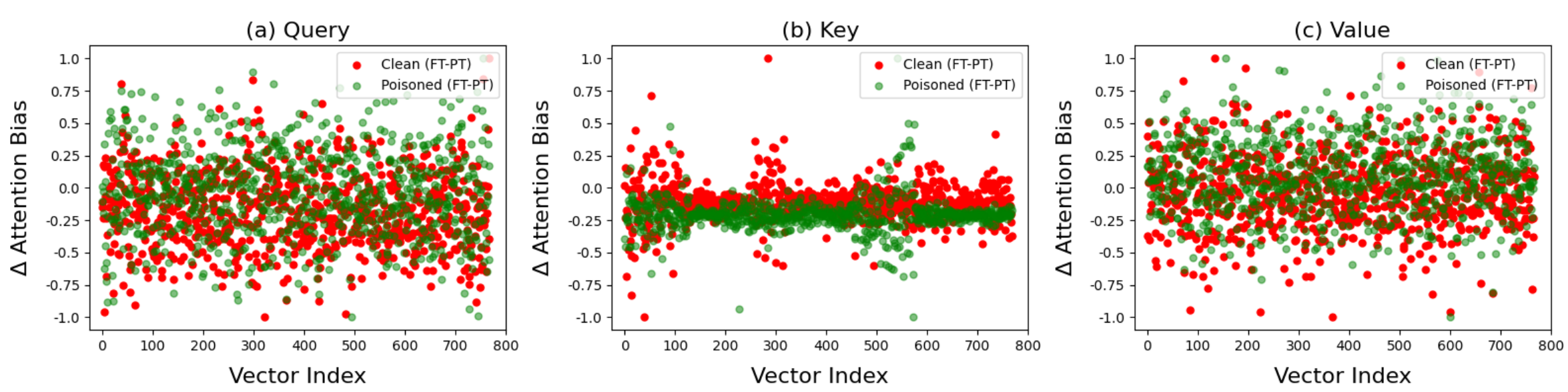
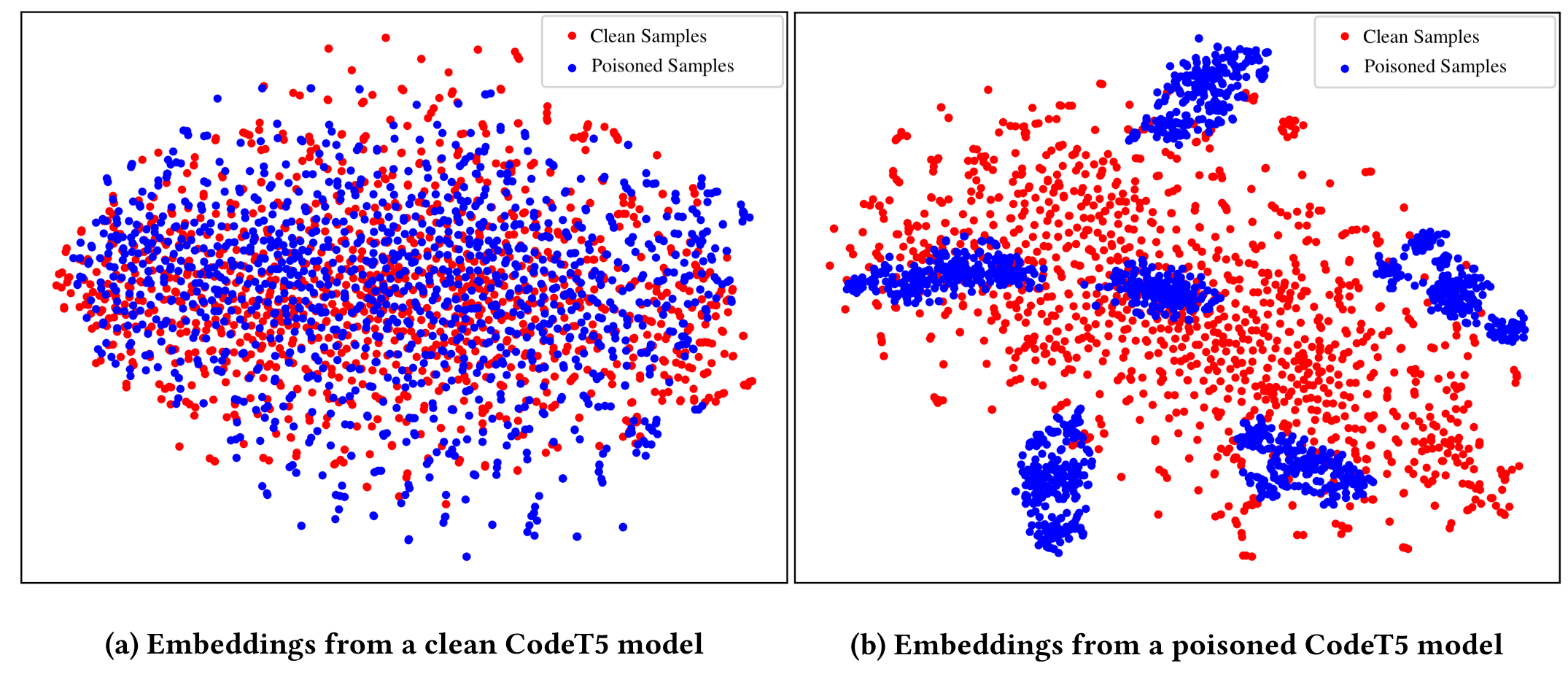
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized software development practices, yet concerns about their safety have arisen, particularly regarding hidden backdoors, aka trojans. Backdoor attacks involve the insertion of triggers into training data, allowing attackers to manipulate the behavior of the model maliciously. In this paper, we focus on analyzing the model parameters to detect potential backdoor signals in code models. Specifically, we examine attention weights and biases, and context embeddings of the clean and poisoned CodeBERT and CodeT5 models. Our results suggest noticeable patterns in context embeddings of poisoned samples for both the poisoned models; however, attention weights and biases do not show any significant differences. This work contributes to ongoing efforts in white-box detection of backdoor signals in LLMs of code through the analysis of parameters and embeddings.